
With an Internet connection comes the fear of getting our data breached. Cyber attacks have become the new norm in recent years. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs will increase by 15% per year over the next five years, reaching USD 10.5 trillion annually by 2025, up from USD 3 trillion in 2015.No wonder why the need for top-notch cybersecurity is increasing on a day-to-day basis.
The trust in outside or inside networks requesting access has gone low to ZERO. And voila, John Kindervag heard us, back in 2010 and coined the term “zero trust,” which centers on the notion that an organization shouldn’t trust anything inside or outside its boundaries.
A zero-trust network operates under the theory that neither users nor computers should be taken for granted because both inside and outside the network there are potential attackers. User identity, rights, and the identity and security of devices are all verified by Zero Trust.
Table of Contents
ToggleWell, let’s cut to the chase and understand, What is ZERO TRUST SECURITY, deeply!
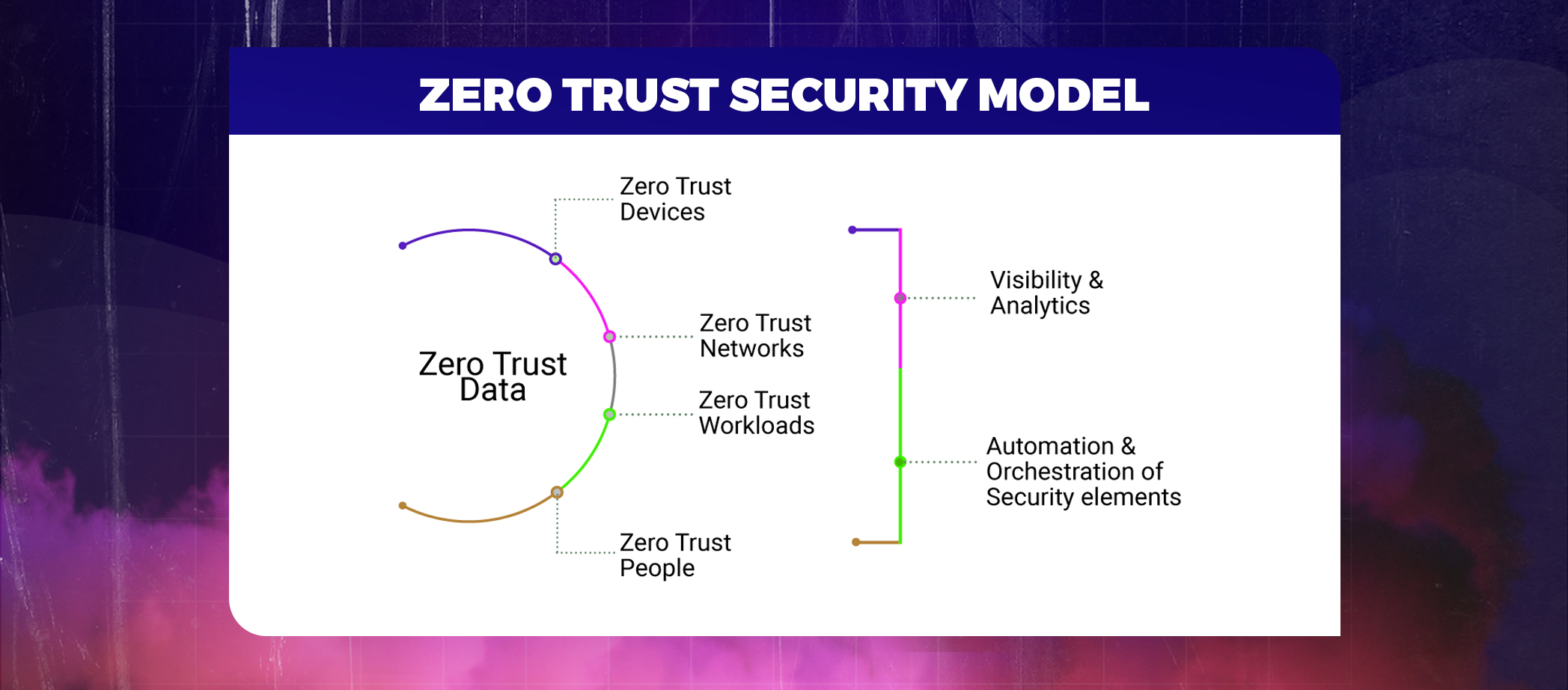
Zero trust is a security concept that states that no user or device trying to access the firm network, whether physically or digitally, should ever be trusted. It is a security framework that requires all users, inside or outside the organization, to be authenticated, authorized, and validated for security configuration before granting access to applications and data. The zero trust model exceptionally challenges modern-day security problems including remote working, ransomware threats, and cloud transformation.
Core principles of the zero trust model
- Never trusting and always verifying
- Consider the ongoing threats to the network
- Authenticate users by least privilege access
- Establish end-to-end analytics
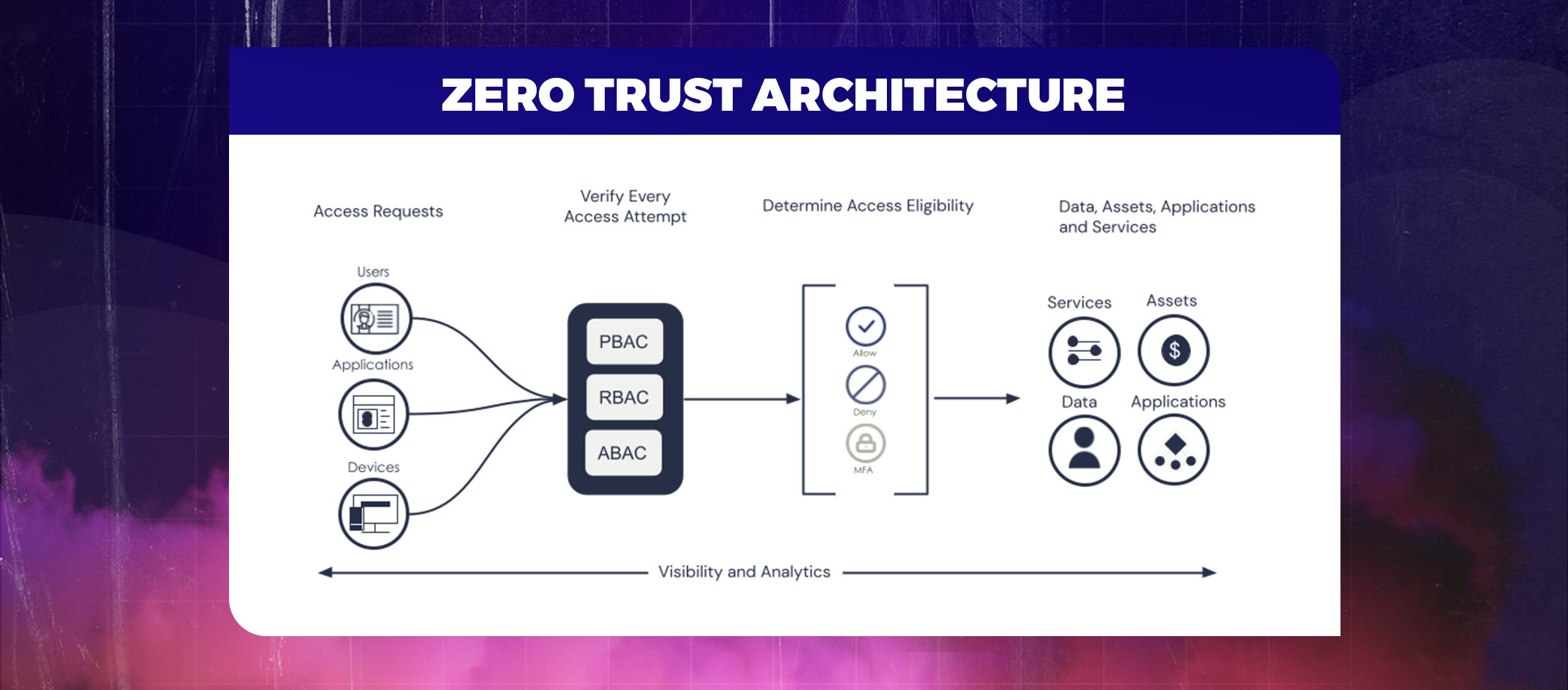
Zero Trust Architecture:- One of the best practices for modernizing Federal Government Cybersecurity
The market for zero trust security was estimated to be worth USD 19.8 billion in 2020, and from 2021 to 2028, it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 15.2%.
Zero Trust Architecture- Explained in points
- Designing the cyber security infrastructure based on the Zero Trust model.
- No component of the network should ever be trusted when building it, regardless of whether the request originates inside or beyond the boundaries.
- Gaining trust only when the users prove their identity by showing their credentials.
- Considering the simplest requests as potential threats.
- Taking into account multi-factor or multi-authorization factors.
- Recheck the credentials on the new access request.
Also Read : Top 10 Considerations in Cybersecurity Risk Management
Zero Trust Security BENEFITS
Zero-trust architecture offers a lot. Such as a considerably more secure environment that safeguards against unauthorized access to critical data and digital assets.
Let’s find out the other benefits of the Zero Trust Security Model-
BYE-BYE RISK
When using a zero-trust security architecture, no apps or services are allowed to communicate until their identity attributes—immutable characteristics that adhere to predetermined trust rules, such as authentication and authorization requirements—have been confirmed.
As a result, zero trust security lowers risk since it reveals what is on the network and how its assets are interacting. A zero trust strategy eliminates overprovisioned software and services as baselines are created and continuously verifies the “credentials” of every communicating assets to further decrease risk.
Got high privacy standards
In a zero-trust architecture, every connection is shielded from the internet, lowering the risk of exposure and exploitation. Compliance with privacy regulations and laws including FISMA, HIPAA, PCI, GDPR, and CCPA is well established since invisibility results in fewer audit findings.
Micro-segmentation, an element of zero trust security, uses precise limitations to distinguish between regulated and unregulated data, allowing the establishment of perimeters.
Boost Data Security
One of the core principles of Zero Trust security is authenticating users by least privilege access. This helps in preventing malicious software or rogue personnel from acquiring access to a sizable area of your network.
Gaining access in a zero-trust security model is like gaining trust. And without trust, the cyber attacker won’t be able to gain access to your data and breach it.
Identity is a Priority
Remote work is highly accepted and spreading across tech giants. With users spread across the world and data on the cloud, there is a significant increase in the risk of companies’ security breaches.
But, thanks to the zero trust security model, where identity is the core perimeter and is attached to users, applications, and devices seeking access, strengthening the security.
Looking for a cyber security experts
Core components of ZERO TRUST ARCHITECTURE (ZTA)
- Policy Engine- decides whether to grant access to any network resource.
- Policy Administrator- Executes access decision
- Policy Enforcement Point-PEPs serve as a system portal for establishing, maintaining, and severing connections between authenticated users and the resources they have access.
How to implement zero trust security?
- Outline the defensive surface
- Illustrate the transactional flows.
- Establish a network with zero trust.
- Implement the Zero Trust policy
- Follow up on the network and maintain it.
FINAL THOUGHTS
The “Never Trust, Always Verify” tenet underlies the Zero Trust security approach. It is a more secure and trustworthy method to defend businesses from cyber threats since it continuously checks for identification and verification. This framework could appear complex, but it is the most straightforward one when teamed with the right technological partner.
With PeoplActive‘s cybersecurity consulting service, you can protect your business against data breaches. To eliminate risks and maintain the security of your business, we develop comprehensive security plans and offer ongoing support.
Get in touch
YOU HAVE DATA
WE HAVE A WAY TO PROTECT DATA




