
As the utility sector embraces digitization, it is also becoming more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Companies have adopted operational technology (OT) and made large investments in big data, cloud computing, and IoT to better manufacture and accelerate product delivery. However, this has increased their attack surface and exposed the infrastructure to cybersecurity threats.
In this blog, we would be discussing the cyber risks utility companies face, the possible damages, the overall readiness of the industry to meet those risks, and what are the most effective solutions to counter cyber attacks on utilities.
Cybersecurity and threat detection remain important priorities as we move towards 2023. Both large and small firms are nonetheless concerned about data breaches and the theft of critical information. According to an IBM analysis, just in 2022, the average cost of data breaches hit $4.35 million globally, up 2.6% from the previous year.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Table of Contents
Toggle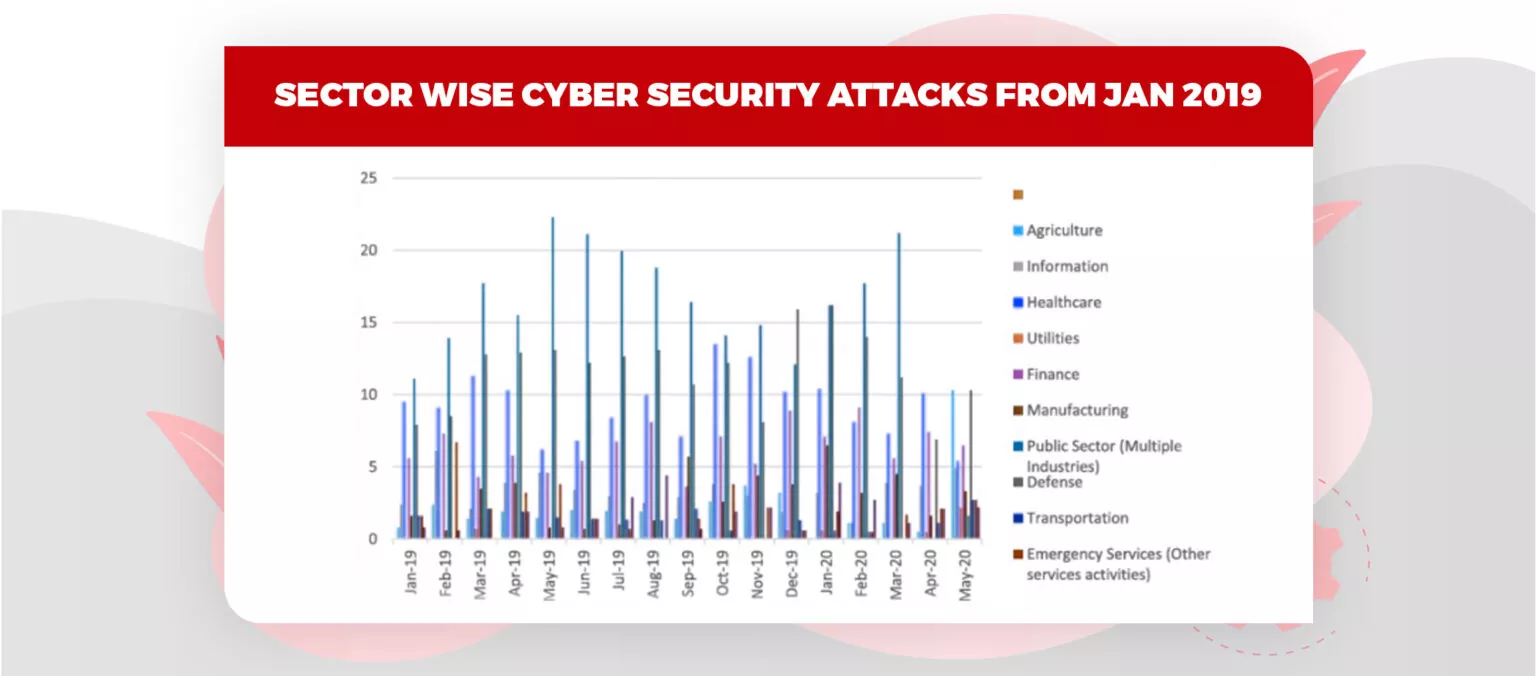
Images Source: Springeropen
What is Cyber Security?
The goal of cybersecurity is to protect the data of your company from intrusions by malicious insiders and outsiders. It might include a collection of methods, tools, frameworks, and procedures used to safeguard networks, computers, software, and data from unwanted access or destruction. Any cybersecurity strategy should aim to protect data integrity, availability, and confidentiality. An organization’s reputation can be harmed (or even destroyed) by cybersecurity concerns in many ways. There is a chance that a hacker will get access to private data like bank or credit card numbers.
What is the Utility Sector?
The utility sector refers to a set of companies that are engaged in offering basic amenities, such as electricity, water, sewage services, dams, food, and natural gas. The utility sector encompasses a wide range of companies in different industries. They include manufacturers, providers, and suppliers such as:
- Energy companies
- Electricity companies
- Water companies
- Food manufacturing companies
- Natural gas companies
- Sanitation and waste disposal companies
The increasing use of software in OT (operational technology) such as programmed gas turbines and software-managed brownfield engine exchanges – has extended the attack surface for hackers to exploit. Also, the operational systems at utilities often take 10-20 years to upgrade or patch. Therefore, any software vulnerability in these systems remains exploitable for several years. Along with this, utility companies can have dozens of remote sites maintaining a continuous flow of data from a central HQ to multiple sub-networks. This shows that the IT security issue also stays in this sector. Utility companies have a large amount of valuable customer data such as credit card information and home addresses etc. that also increase the chances of cyber attacks on utilities data.
Critical security concerns facing the energy & utility industry
Utility Cybersecurity Challenge 1: Securing basic infrastructure and the grid
Our energy and utility basic infrastructures are encountering a significant shift towards the utilization of smarter and advanced technologies to counter the resource requirements of a growing population.
Operational Technologies (OT), like Industrial Control Systems (ICS) and SCADA, are connected to a wider network and are being increasingly targeted by hackers. As per reports, there is an absence of maturity in cybersecurity safety approaches while merging OT and IT that increase chances of cyber attacks on utilities.
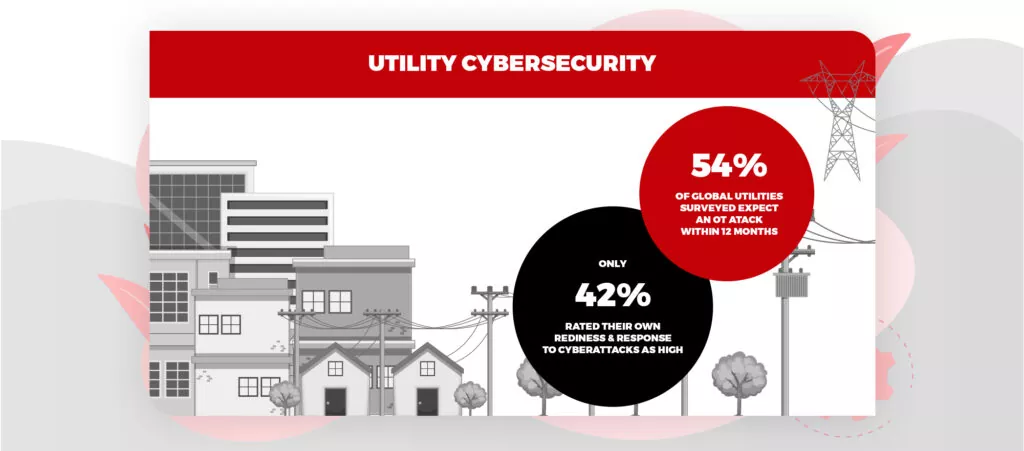
Image Source: Weforum
Utility Cybersecurity Challenge 2: IoT and Cyber-Physical Attacks
One reason for this is the expanding utilization of internet-enabled gadgets and remote sensor networks by the energy and utility industry. Modern industrial systems are dependent on the utilization of the cyber-physical system. ICS (industrial control system) units are progressively turning out to be important for the more extensive Internet of Things (IoT), permitting them to control actual frameworks utilizing digital strategies.
Today, mobile applications are also being utilized as a remote control point. In doing so, we have made many new entry points for malicious activities. The sorts of attacks found in the utility sector encompass data breaches, defacement, physical harm, and information tampering. A review into the utilization of mobile applications to control ICS found more than 100 vulnerabilities, of which 20% could be utilized as a vector for malicious control of the industrial process and weakens cybersecurity for utilities.
Utility Cybersecurity Challenge 3: Automation, AI and security
Like every other industry, the utility industry is also utilizing advanced and smart technologies to smooth out processes such as big data, and artificial intelligence. Automation will bring new security and protection worries, as AI and ML capture personal as well as other critical data to build better and more enhanced frameworks. Total of this information may likewise draw new worries, particularly as far as security.
Utility Cybersecurity Challenge 4: Cyber Security Skill Shortage
Utility and energy organizations belong to a traditional industry. Their core business isn’t security. However, not focusing on the cyberthreats within the organization can undeniably complicate things and may leave the business helpless.
As the utility sector is embracing digital transformation, it also requires a team having new skills and proactive plans to overcome the unprecedented cyber threats.
3 Steps To Improve Cybersecurity in Utilities Industry
Assess Your Risk Portfolio
One of the initial steps a utility can take to launch a fruitful, risk-based security strategy is to do a complete organizational review. This would include building a cybersecurity plan intended to recognize critical resources and the risk they would cause whenever compromised or lost.
With this data, utility companies become aware of the extent of the risk for delivery of services and can be better ready for it. With a better understanding of risk tolerance, these organizations can focus on cloud cybersecurity protection exercises, empowering utility leaders to settle on more advanced choices about expenditures on cybersecurity for utilities.
Pervasive Security Architecture
Advanced systems and devices are continually added to improve the performance, flexibility, and resiliency of the grid,
Communication infrastructure was set up before security was even considered. With the arrival of IoT, the edge of the organization continues to develop and extend. Issues and weaknesses prompted wireless cameras and insecure routers leading to DDoS attacks. Shielding the infrastructure from the steadily expanding number of sensors and gadgets will guarantee grid stability. Identification of resources, legitimate access control, and data flow segregation will be in every way pivotal administration that should be planned and architected as the edge of the organization proceeds to develop and grow.
Utilize Common Security Tools
Utilities use Network firewalls in their security models to shield IT and OT frameworks from cyber threats. Firewalls block external threats and control traffic to distinct interior zones of the network. Limits for these trust zones are especially significant for utility organizations that require both IT and OT frameworks to operate.
Most of the firewalls are capable of inspecting the network traffic to and from the system which helps us to block inappropriate traffic. DPI (Deep Packet Inspection) firewalls apply deep and detailed inspection to the network traffic. These firewalls are used to isolate malicious data messages from routine control messages.
Haven’t you yet formed a Cybersecurity team?
Having a cybersecurity expert team has become a necessity for every business. Cybersecurity for utilities is equally important and crucial to safeguard the entire production and delivery process. Are you looking for cybersecurity professionals? If so, PeoplActive is a one-stop solution for you.
PeoplActive is an IT consulting company and also offers staffing/staff augmentation services to our clients for both PERM and Remote roles. We specialize in the cloud and cyber security roles however, that does not limit our expertise, we also assist our clients with different complex IT roles like Full Stack, Mean Stack, Data Engineers, iOS or Android, etc.
Our tech-savvy recruiters are well versed with the latest technology, programming knowledge, and other skills which help them better understand the job description and bring exceptional talents to your dream team.
- Geographies – US, India, UAE, and ANZ.
- Avg. placement Percentage – More than 90%
- Specialization – Cloud Platforms (Azure, AWS, GCP, etc.) Cyber Security, DevOps, Architect, Data Engineers, etc.
- Joining Turn Around – 2 to 4 weeks.
- Flexible hiring model – Contractual or Permanent.
We hope you found the blog useful and informative. In case you have any talent-hiring requirements, let us know today. Looking forward to hearing from you.




