In this decade, there has been a transformative shift from on-premise computing to cloud computing, enabling systems to be centrally managed and accessible while enhancing security and collaboration. We are currently seeing a transition from cloud computing to edge computing as we approach the beginning of a new decade.
Like the cloud, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence, edge computing is a buzzword. Edge computing, in other words, facilitates the decentralization of networks. Undoubtedly, the upcoming trend in technology is edge computing.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Edge Computing?
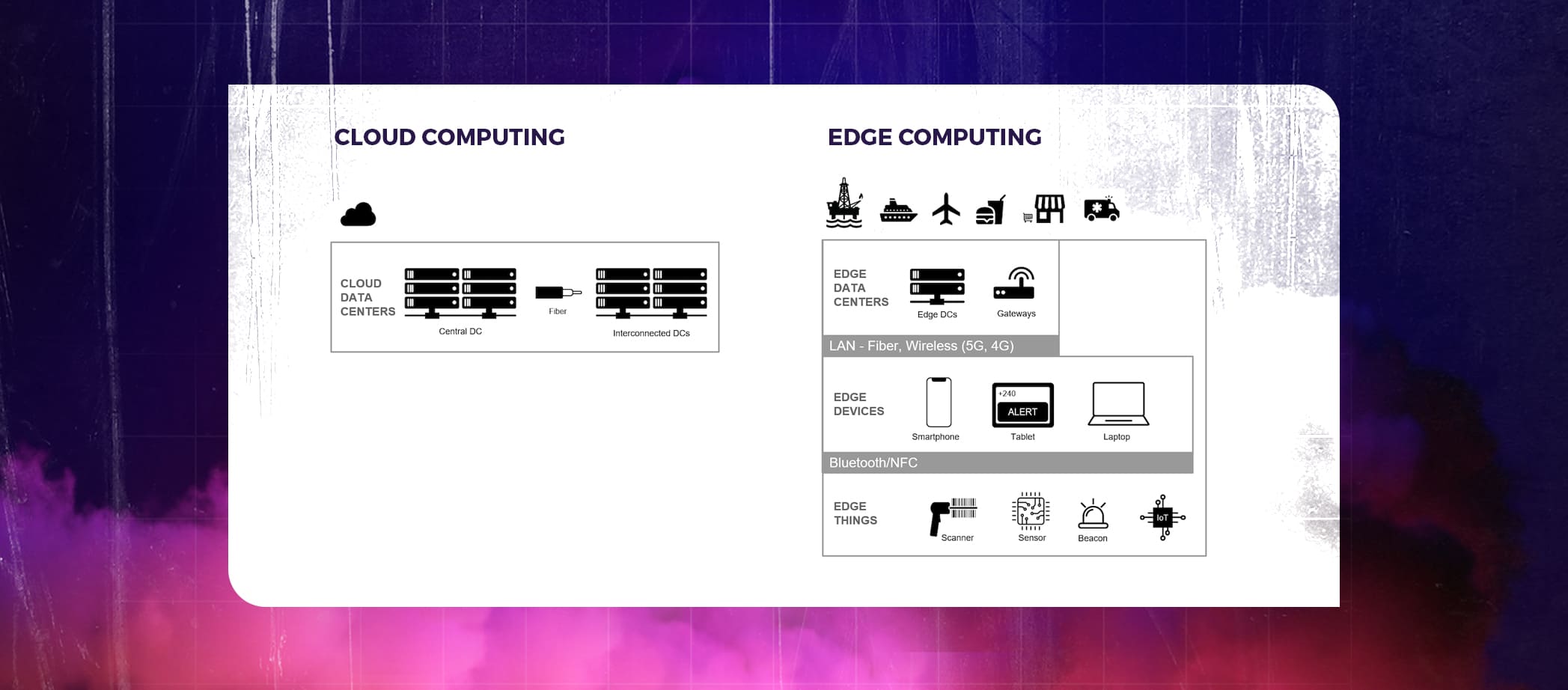
Edge computing is a distributed information technology (IT) architecture where user data is handled by the network’s edge. In contrast to Cloud Computing, which involves computing occurring at a central location, Edge Computing refers to computations that occur at the “Outside Edge” of the internet. It often takes place close to the data source. 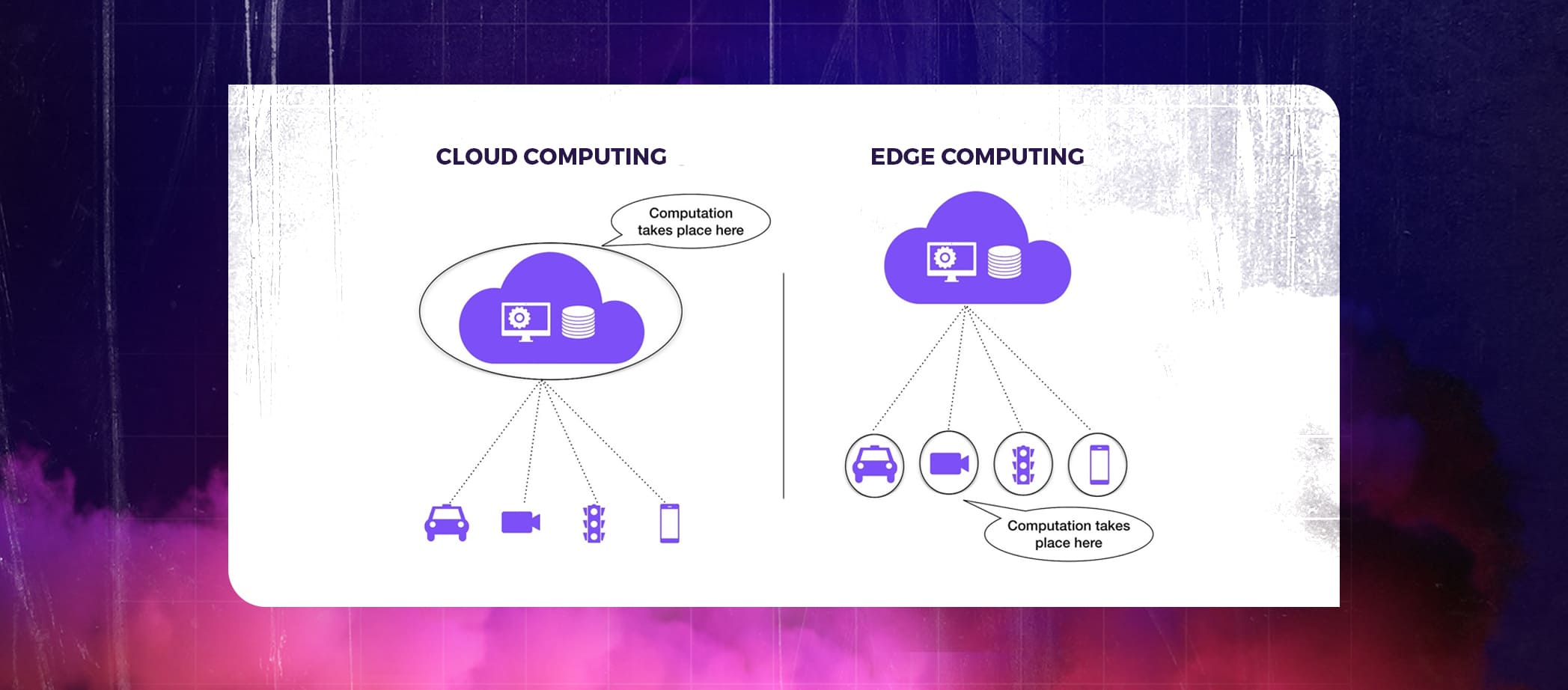
A self-driving car is the ideal illustration of edge computing. Observing the road in real-time and stopping if someone steps in front of the car is necessary for cars to travel down any road securely. In this scenario, edge computing is used to analyze visual input and reach a conclusion. 
This illustration focuses on speed as a major driver of edge computing. Cloud solutions that are centrally managed offer simple access and collaboration, but because the servers are centrally managed, they are far from the data sources. A self-driving car needs to make decisions and take action as quickly as possible after gathering data from sensors.
Also Read : The six most damaging mistakes in cloud economics to avoid
Types of Edge Computing
We will now shift our focus to the various types of edge computing.
Sensor Edge
In a typical closed-loop system, sensors are the first point from which events are transmitted to the backend systems. When operating a video camera, for instance, the best practice is to send out live streams whenever there is motion.
Device Edge
Customers use several types of devices to carry out specific types of functions. X-ray machines, vending machines, motors, and other particular gadgets are some examples. Data from these devices can be gathered and evaluated to aid in the smooth operation of these devices. In this instance, the computing resources are deployed close to the devices so that workloads can be processed with ease.
Router Edge
If we consider a router’s main purpose, it is to deliver packets across networks. They effectively serve as a defining factor between internal networks and external systems. Few business routers come with built-in computing modules and support for hosting applications.
Branch Edge
A branch is described as a location that is distinct from the main office and established to carry out a certain type of task. Each branch utilizes a varied set of programs according to its needs and the function that the particular branch performs. For instance, in the retail industry, this system might be a point-of-sale program utilized at the storefront.
Since these apps are essential to the operation of the business, they must be hosted on an edge network at the branch level to prevent any latency from affecting user access to the applications.
Enterprise Edge
Computer resources can be utilized by the many branches of a business that operates in a distributed environment with branches spread out throughout a place. The main goal of this is to facilitate management and produce economies of scale.
In this approach, edge computing devices are hosted on a shared site that is connected to the company network rather than being placed at each location.
Datacenter Edge
As of right now, more clients are migrating from their current data center to the cloud network. As a result, we are observing the emergence of small data centers, enabling the edge to be deployed closer to the client and facilitating quick deployment and data portability on specific occurrences.
Cloud Edge
Providers of cloud services offer targeted services that are more convenient for the client. This is done to make sure that processes like content delivery are running as efficiently as possible. Although CDNs were not designed to handle typical workloads, they are occasionally used to describe cloud edges.
Also Read : How Is The Cloud Revolutionizing the Media Industry?
Visualizing an Edge Computing Architecture
Edge computing utilizes tiered, edge data centers and, when suitable, embeds data storage directly on devices to shift data processing and storage closer to applications and client devices.
Applications are protected from disruptions in the central and local data centers by this layered strategy. As local connectivity improves, each tier uses it to synchronize data both within and between tiers, which is more dependable. Applications that are always quick and always on are powered by edge computing.
Understanding the notion is made simpler by picturing edge architectures as a collection of layers. Check out the illustration below:
Why move from Cloud to the Edge?
A new technology called edge computing will not only save time but also money on maintenance and other expenses.
Speed
Edge devices gather data in cloud computing and deliver it to the cloud for additional processing and analysis. Devices at the Edge primarily send unprocessed data to the Cloud and receive processed data from it. The Cloud is where the main work is done. This kind of architecture might be appropriate for applications where users can tolerate a two or three-second response time. However, this is inappropriate for applications that need to react quickly, particularly those that require real-time response, like in a self-driving car.
Bandwidth
Since most processing is done at the Edge and only the final product is transferred to the Cloud, less data transmission bandwidth is needed. Consider a smart parking system that employs cloud computing infrastructure to determine the number of available parking spaces. The cloud may receive a live video feed or still, photos, say in 1080p, transmitted every few seconds. Imagine the network bandwidth and data transmission costs needed for this solution per hour, with continuous network transfer of large amounts of raw data:
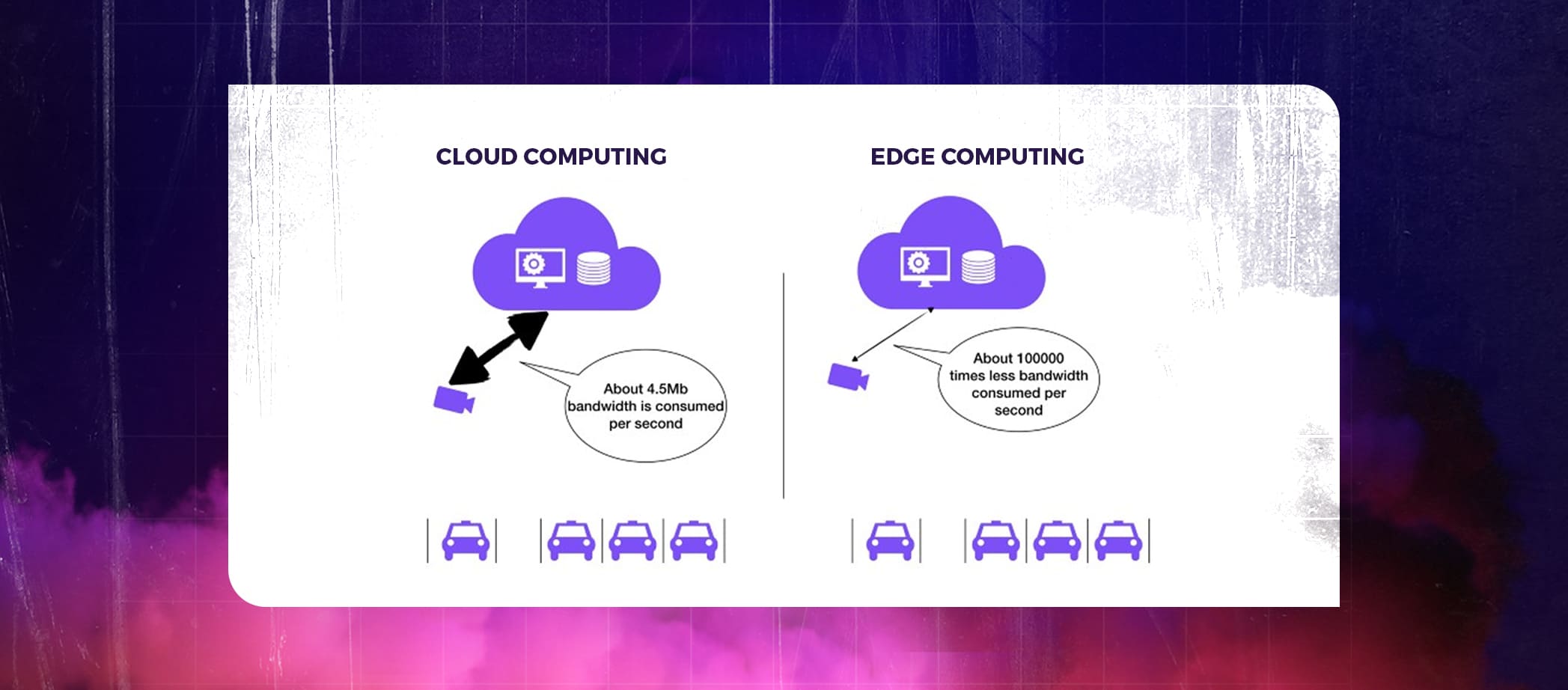
In contrast, if the smart parking system uses edge computing, it would just need to send an integer representing the number of parking spots available to the cloud every few seconds, requiring less bandwidth and costing less to transmit data.
Scale
IoT increases the number of systems, and more systems need more bandwidth and put more load on centralized servers. When one IoT device is added to a cloud computing system, the bandwidth requirement, and cloud computing power increase.
Let’s use the smart parking system example from above, which streams a live 1080p video feed to the cloud. The client wants to implement this technology in 10 more parking lots. As the demand for centralized servers grows as a result of the influx of data from 10 more cameras, they must increase their network bandwidth and require around ten times more processing power and cloud storage space to make this possible. As a result of the increased network traffic, the uplink bandwidth becomes constrained. Scaling is therefore expensive because every extra device increases network traffic, bandwidth, and cloud resource usage. 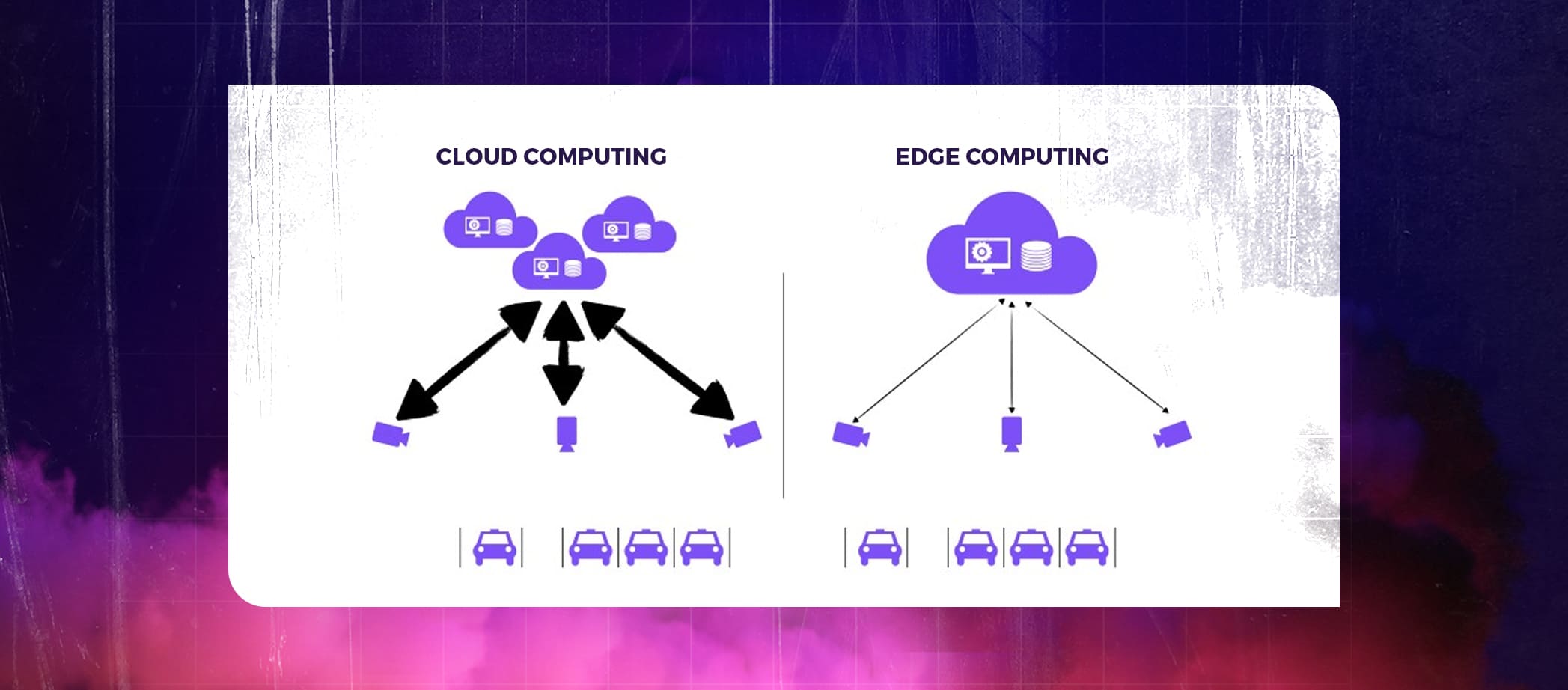
Looking for a Cloud experts
Applications of Edge Computing
The world depends on the Internet today for everything from tiny to large-scale operations, which has led to a decrease in the cost of IoT devices like sensors and computational power. In this manner, more devices will continue to be linked to the Internet. Edge computing will become in demand as a result of the availability of more connected devices. Edge computing has the potential to improve the following sectors: 
Edge computing, IoT, and 5G possibilities
Edge computing is still developing, utilizing new techniques and technologies to improve its performance. The edge availability trend is arguably the most significant one, and by 2028, edge services will be accessible globally. In the upcoming years, wireless communication technologies like 5G and Wi-Fi 6 will also have an impact on edge deployments and utilization. These technologies will make wireless networks more flexible and affordable while also enabling virtualization and automation capabilities that have not yet been fully explored, like improved vehicle autonomy and workload migrations to the edge.
The emergence of IoT and the sudden glut of data such devices produce brought edge computing to public attention. However, because IoT technologies are still in their infancy, edge computing’s progress will also be impacted by the advancement of IoT devices. One example of such future alternatives is the development of micro-modular data centers (MMDCs).
As we seek higher performance and more innovation from our computing systems, software architectures have changed from on-premise computing to cloud computing and now to edge computing. The market for edge computing is expanding as we outgrow our present cloud-based architectures, propelled by factors such as the desire for real-time applications and the cost demands of IoT, among others. In the upcoming years, the software business will take on a new look because of this trend. Welcome to the future!
Edge Computing will play a major role in the transformation of today’s business. Haven’t you adopted this technology yet? We hope reading this blog must have guided you on how you can ease your business operations with cloud automation.
Are you looking to hire cloud engineers? Well, PeoplActive not only brings the perfect talent but also offers consultation services on your projects to help you create a roadmap. Let us know your requisitions to hire cloud engineers at competitive prices in the market.
Get in touch
A Call for Cloud
Take the guesswork out of your next best Cloud decisions