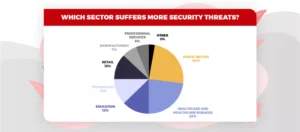
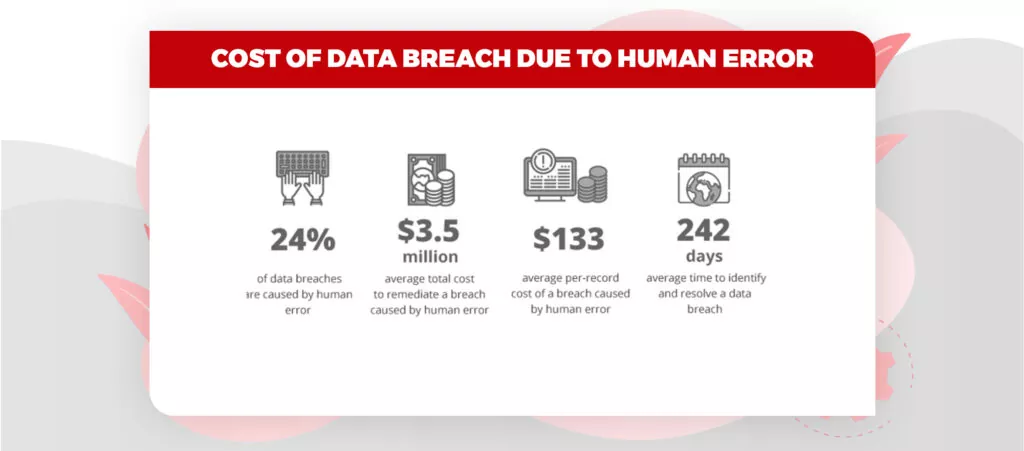
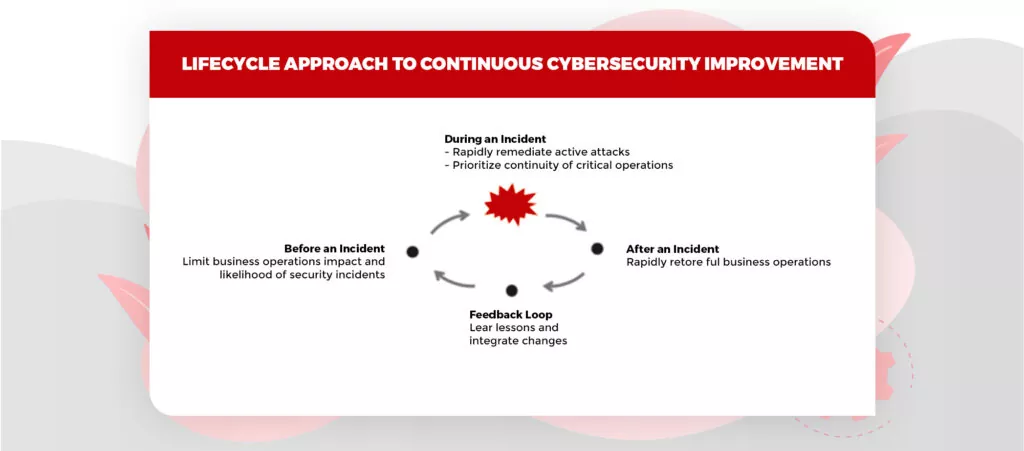
With so many digital wallet options, Fintech Cybersecurity Risks like fraudulent transactions, extortion, denial of service attacks, and credit card fraud have increased. These cyberattacks are powerful enough to put the financial sector at systemic risk. Some of the most well-known cyberattacks the financial sector has seen to date have impacted critical economic infrastructures. These cyberattacks have the potential to compromise important company data and intentionally destroy hardware, negatively affecting services. Cybersecurity threats affect nearly all elements of the FinTech ecosystem. They might expose different technologically savvy financial institutions, FinTech start-ups, and monetary clients within the FinTech ecosystem. Technology developers also need to be conscious of any cybersecurity issues that could exploit security vulnerabilities and flaws in the technology they are creating.
This blog reveals various cybersecurity risks faced by the FinTech industry and offers an in-depth analysis of the groups and individuals responsible for those risks.
Let’s Go and find out!
Importance of Cybersecurity in FinTech
Fintech is a term used in contemporary language within the financial industry to describe the application of technology and innovation for financial services and systems.

Fintech apps like Venmo, Robinhood, Chime, PayPal, MoneyLion, Mint, and Card Curator have disrupted and changed the banking and financial services industry in recent years. Global consumers already use up to 75% of fintech services, and that percentage is anticipated to grow as more individuals use contactless payments, mobile banking, micro-investing, online lending, travel hacking, and other fintech-enabled financial practices. Fintech applications are treasure troves for online thieves seeking to steal priceless personal and financial information.
FinTech Cybersecurity Risks and Challenges
It’s critical to recognize new issues in the realm of Cybersecurity to comprehend how to make it impenetrable to planned cyberattacks.
Cloud Computing Issues
Most online financial services, including payment gateways, net banking, digital wallets, and form filling, are carried out via a cloud-based computing system. Although cloud computing provides advantages such as scalability, speed, and accessibility, the volume of data pouring into it makes it the ideal cover for cyberattacks. As a result, it requires different security measures than conventional local data centers. It is crucial to pick a trustworthy and safe cloud service provider that can customize the cloud to meet the needs of the client.
Malware Attacks
The most prevalent type of cyberattack is malware. Malware has advanced significantly, making it harder to identify and eradicate. In contrast to other attacks, malicious software can enter through a variety of channels, including emails, third-party software, suspicious websites, and pop-up windows. It is particularly hazardous because of its deadly transmission and spread rates, which can bring down entire networks. Because of this, it’s crucial to pick cybersecurity infrastructure providers with regularly updated malware detection software and capabilities like automated real-time malware detection.
Third-Party Access
FIs and banks frequently use third-party services and software for a variety of applications. Since these programs are connected to the major systems of the organizations, they serve as entry points for hackers posing as authorized staff members or customers of a third party. Banks must use caution when selecting a dependable third-party solution to help fintech overcome cybersecurity concerns.
System Complexity and Compatibility
Large financial institutions and banks sometimes have multiple branches and headquarters around the globe, each of which is outfitted with infrastructure from various producers and developers. These systems are linked together, but they might not be compatible with one another or they might forge complicated relationships, which would leave gaps in the network. These flaws serve as the entry points for cyberattacks.

Money Laundering Risks
Since they have grown in popularity in recent years, cryptocurrencies have become one of the biggest cybersecurity challenges facing the finance industry. Cryptocurrencies can be used to launder money produced illegally and the source of the funds can be hidden. Additionally, bitcoin transactions may be a target for fraud and hacker access points for data theft, resulting in significant losses and issues with law enforcement. Therefore, banks and FIs who work with cryptocurrencies should exercise caution and only trade on secure platforms.
Identity Theft and Authentication
Banks and FIs frequently utilize methods like one-time payments, biometrics, passwords, and other types of authentication to provide security and confirm identity. These techniques do have the disadvantage that they can frequently be copied, opening the door for hackers to steal substantial amounts of money. Although these techniques are helpful, banks and FIs must apply a variety of verification gateways based on various concepts to prevent invasion.
Online Digital Platform
The majority of banks and FIs now use internet platforms. This indicates that PCs and mobile devices—through which the majority of users access their accounts—are vulnerable to hacking. As a result, even if the bank’s network is safe, it is unable to identify a compromise in the user’s device. Customers must therefore complete significant transactions using computers and other devices that offer greater security. Additionally, installing antivirus software with real-time detection and secured browsing is advised when using these devices for banking.
Compliance
Fintech must adhere to regulatory and compliance regulations depending on the kind of service. In a similar vein, rules requiring businesses to “know their consumers” require them to keep an eye out for illicit activity like tax evasion and money laundering. The rules are centered on certain services including insurance, lending and borrowing, stock market trading, and financial advising. Nevertheless, all institutions must comply with certain standards. These rules are in place to uphold a specific level of security for the customers’ money and personal information. Additionally, breaking these rules or failing to comply with them might result in penalties and government action.
Therefore, businesses that want to address the current cybersecurity issues facing the fintech industry must adhere to rules as closely as possible.
Conclusion
FIs deal with millions of bytes of data each day that pertains to private, personal, and financial information, making them a gold mine for hackers. As a result, cybersecurity threats will always be a serious concern. Therefore, it is crucial for cybersecurity and data protection firms to always be in the lead when it comes to coming up with creative solutions to cybersecurity concerns in fintech, thereby regaining the trust of the platform’s users.
With the assistance of a Cyber Security Engineer, you can defend your company against these novel risks. With PeoplActive you can hire a skilled Cyber Security Engineer within 48 hours.