Introduction
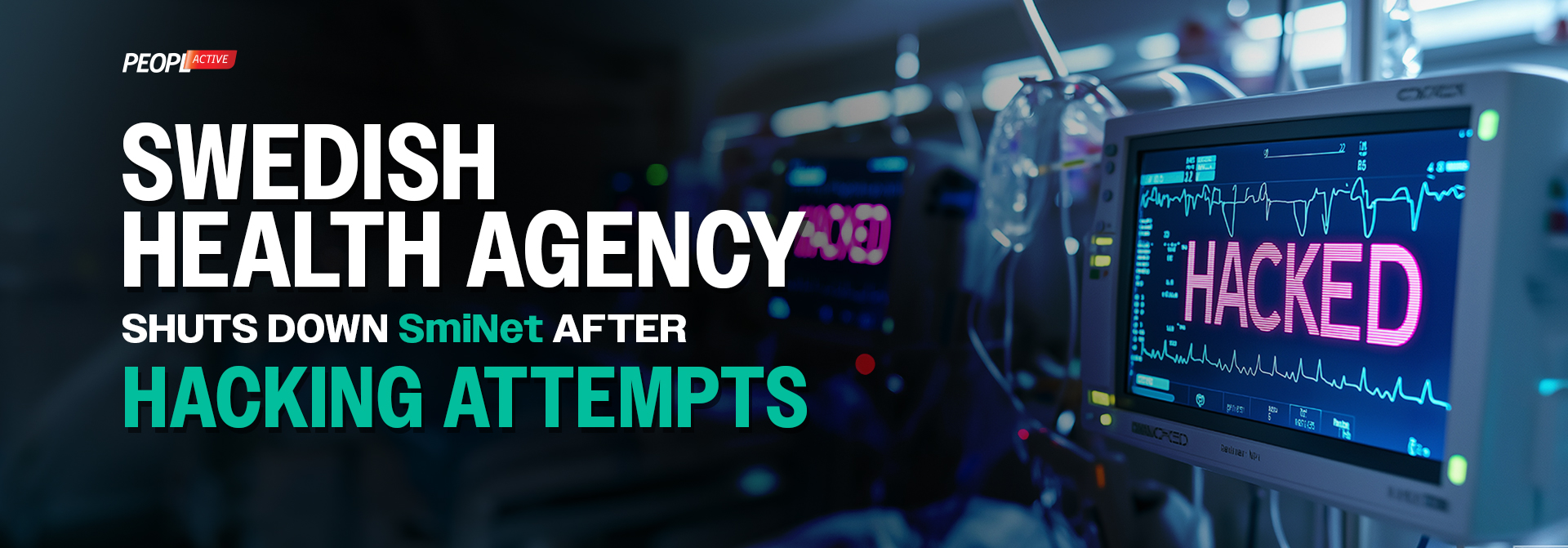
Cyber threats targeting healthcare systems are on the rise, with cybersecurity for healthcare providers becoming a critical concern worldwide. A recent example of this growing threat landscape is the Swedish Health Agency’s decision to shut down SmiNet, its national infectious disease database, after facing multiple hacking attempts. This breach raises alarms about the security of medical data, particularly in the realm of medical device cybersecurity and the broader field of cybersecurity and medical devices.
This blog explores the implications of the cyberattack on SmiNet, the vulnerabilities in healthcare cybersecurity, and best practices for protecting sensitive patient information.
The SmiNet Cyberattack: What Happened?
Understanding SmiNet’s Role in Sweden’s Healthcare System
SmiNet is a crucial digital infrastructure in Sweden, designed for:
- Tracking infectious diseases such as COVID-19, tuberculosis, and influenza.
- Collecting and storing patient data to monitor disease outbreaks.
- Facilitating public health responses based on real-time data analytics.
As a key system for Swedish healthcare, any cyberattack against SmiNet threatens not only patient data but also the nation’s ability to manage public health crises effectively.
Details of the Hacking Attempts
The Swedish Public Health Agency reported multiple hacking attempts on SmiNet, prompting an immediate shutdown of the system. Key aspects of the attack include:
- Unusual access patterns detected, suggesting an attempt to breach sensitive data.
- Repeated cyber intrusions over several days.
- Potential data exposure of patient health records and disease tracking information.
- Preventive shutdown to mitigate damage and prevent further intrusions.
While no confirmed data leaks have been reported, the breach underscores the pressing need for stronger cybersecurity for healthcare providers.
Cybersecurity Risks in Healthcare Systems
Why Healthcare Is a Prime Target for Cybercriminals
The healthcare industry is an attractive target for cybercriminals due to:
- High-value data: Medical records contain personal, financial, and insurance information.
- Outdated security measures: Many hospitals and agencies still operate on legacy IT systems.
- Interconnected networks: Digital transformation has increased connectivity between hospitals, labs, and research institutions.
- IoT and connected medical devices: Many healthcare facilities rely on networked medical devices, increasing potential attack surfaces.
Medical Device Cybersecurity Concerns
The attack on SmiNet is a stark reminder of the need to enhance medical device cybersecurity. Many connected medical devices operate on outdated firmware, making them vulnerable to cyber threats.
Key Cyber Risks to Medical Devices
- Ransomware attacks: Encrypting patient records and demanding payment for decryption.
- Malware infections: Disrupting medical device functionality and compromising patient care.
- Data breaches: Exposing patient information, leading to identity theft and insurance fraud.
- Remote exploitation: Hackers gaining unauthorized access to medical devices, manipulating their functions.
The Role of Cybersecurity in Protecting Healthcare Infrastructure
Strengthening Cybersecurity for Healthcare Providers
To prevent attacks like the one on SmiNet, healthcare providers must adopt stronger cybersecurity strategies.
Essential Cybersecurity Measures
1. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Reduces the risk of unauthorized system access.
- Ensures additional verification layers for logging into healthcare databases.
2. Regularly Patch and Update Systems
- Prevents exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
- Ensures that security patches are applied to operating systems and medical devices.
3. Strengthen Network Security
- Uses firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Implements network segmentation to isolate critical systems.
4. Encrypt Sensitive Patient Data
- Protects stored and transmitted medical information.
- Ensures compliance with GDPR and other data protection regulations.
5. Conduct Cybersecurity Training for Healthcare Staff
- Educates employees on phishing, social engineering, and other cyber threats.
- Encourages best practices for handling sensitive medical data.
Impact of the Attack on Healthcare and Public Trust
Consequences of Cybersecurity Breaches in Healthcare
The attack on SmiNet has significant implications, including:
- Delayed medical research: Interruptions in disease tracking impact public health studies.
- Disruption of healthcare services: Hospitals and clinics rely on digital systems for real-time data.
- Loss of patient trust: Patients expect healthcare providers to safeguard their private information.
Rebuilding Trust Through Enhanced Security
Steps to Regain Public Confidence
- Transparent communication: Healthcare agencies must disclose breaches promptly.
- Investments in cybersecurity: Governments must allocate funds for better healthcare IT security.
- Public-private partnerships: Collaboration between cybersecurity firms and healthcare providers can improve resilience.
The Future of Cybersecurity and Medical Devices
Emerging Trends in Healthcare Cybersecurity
The evolving cybersecurity landscape necessitates proactive measures:
- AI-driven threat detection: Machine learning algorithms can identify unusual activity.
- Zero-trust security models: Requires verification for every access attempt.
- Blockchain for medical records: Enhances data integrity and security.
Collaborative Cybersecurity Initiatives in Sweden
Sweden is strengthening its cybersecurity framework through:
- National Cybersecurity Centre (NCSC-SE): Improving threat intelligence sharing.
- EU cybersecurity regulations: Aligning with NIS2 Directive and MDR standards.
- Increased funding for digital health security: Investing in secure IT infrastructures for healthcare institutions.
Conclusion
The hacking attempts on SmiNet highlight the vulnerabilities in cybersecurity for healthcare providers, raising concerns about medical device cybersecurity and cybersecurity and medical devices. As cyber threats continue to evolve, proactive security measures must be implemented to protect patient data and healthcare infrastructure.
Strengthening cybersecurity strategies, investing in advanced security technologies, and fostering collaboration between healthcare agencies and cybersecurity experts are critical steps in ensuring a resilient healthcare system. With ongoing improvements, Sweden and other nations can mitigate cyber threats and maintain public trust in their healthcare services.